Loading...
Searching...
No Matches
geometry/surfaces/dvcm-2d-curvature.cpp
This example shows the computation of the VCM of a sequence of 2D digital points forming a 4-connected curve. The absolute curvature is estimated from the diagonalization of the VCM tensor. A red color indicates a strong curvature, flat zones are blue, in-between is yellow.
$ ./examples/geometry/surfaces/dvcm-2d-curvature
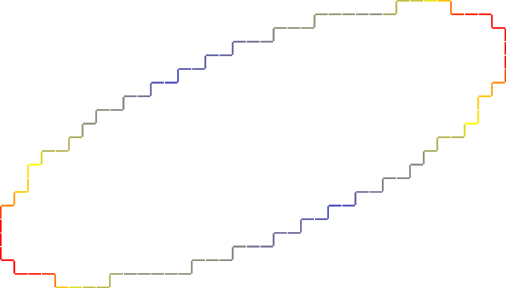
Absolute curvature estimation with Voronoi Covariance Measure.
#include <iostream>
#include "DGtal/base/Common.h"
#include "DGtal/helpers/StdDefs.h"
#include "DGtal/topology/SetOfSurfels.h"
#include "DGtal/topology/DigitalSurface.h"
#include "DGtal/geometry/curves/GridCurve.h"
#include "DGtal/geometry/volumes/distance/ExactPredicateLpSeparableMetric.h"
#include "DGtal/geometry/volumes/estimation/VoronoiCovarianceMeasure.h"
#include "DGtal/geometry/surfaces/estimation/VoronoiCovarianceMeasureOnDigitalSurface.h"
#include "DGtal/geometry/surfaces/estimation/VCMDigitalSurfaceLocalEstimator.h"
#include "DGtal/io/colormaps/GradientColorMap.h"
#include "DGtal/io/boards/Board2D.h"
#include "ConfigExamples.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace DGtal;
{
typedef Curve::SCellsRange LinelRange;
typedef VoronoiCovarianceMeasureOnDigitalSurface<DigitalSurfaceContainer,Metric,KernelFunction> VCMOnSurface;
KernelFunction, CurvatureFunctor> VCMCurvatureEstimator;
// Transform a 4-connected sequence of discrete points into a digital surface.
//string inputSDP = examplesPath + "samples/flower-30-8-3.sdp";
//string inputSDP = examplesPath + "samples/ellipse-20-7-0.4.sdp";
//string inputSDP = examplesPath + "samples/accflower-20-5-5-0.1.sdp";
string inputSDP = examplesPath + "samples/circle-43.sdp";
Curve curve( ks );
fstream inputStream( inputSDP.c_str(), ios::in);
curve.initFromVectorStream(inputStream);
inputStream.close();
DigitalSurfaceContainer* container
LinelRange range = curve.getSCellsRange();
for ( LinelRange::ConstIterator it = range.begin(), itE = range.end(); it != itE; ++it )
container->surfelSet().insert( *it );
trace.info() << " [done] " << std::endl ;
const double R = 40;
trace.info() << "Big radius R = " << R << std::endl;
const double r = 20;
trace.info() << "Small radius r = " << r << std::endl;
const double T = 0.2;
trace.info() << "Curvature thres. T = " << T << std::endl; // threshold for displaying features as red.
Metric l2;
KernelFunction chi( 1.0, r );
VCMCurvatureEstimator estimator( ptrSurface );
estimator.init( 1.0, ptrSurface->begin(), ptrSurface->end() );
// Flat zones are blue, more curved zones are yellow till red.
GradientColorMap<double> colormap( 0, T );
Board2D board;
for ( Surface::ConstIterator it = ptrSurface->begin(), itE = ptrSurface->end();
it != itE; ++it )
{
double curv = estimator.eval( it );
curv = std::min( T, curv );
board << CustomStyle( it->className(),
<< *it;
std::cout << curv << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
// //
Aim: This class specializes a 'Board' class so as to display DGtal objects more naturally (with <<)....
Definition Board2D.h:71
Aim: Smart or simple const pointer on T. It can be a smart pointer based on reference counts or a sim...
Definition CountedConstPtrOrConstPtr.h:95
Aim: Represents a set of n-1-cells in a nD space, together with adjacency relation between these cell...
Definition DigitalSurface.h:140
Aim: implements separable l_p metrics with exact predicates.
Definition ExactPredicateLpSeparableMetric.h:88
Aim: This class template may be used to (linearly) convert scalar values in a given range into a colo...
Definition GradientColorMap.h:120
void addColor(const Color &color)
Aim: A model of CDigitalSurfaceContainer which defines the digital surface as connected surfels....
Definition SetOfSurfels.h:74
Aim: Represent adjacencies between surfel elements, telling if it follows an interior to exterior ord...
Definition SurfelAdjacency.h:66
Aim: This class adapts a VoronoiCovarianceMeasureOnDigitalSurface to be a model of CDigitalSurfaceLoc...
Definition VCMDigitalSurfaceLocalEstimator.h:83
Aim: This class specializes the Voronoi covariance measure for digital surfaces. It adds notably the ...
void saveSVG(const char *filename, PageSize size=Board::BoundingBox, double margin=10.0) const
Definition Board.cpp:1011
DGtal is the top-level namespace which contains all DGtal functions and types.
Definition ClosedIntegerHalfPlane.h:49
Trace trace
STL namespace.
Custom style class redefining the pen color and the fill color. You may use Board2D::Color::None for ...
Definition Board2D.h:279
Definition Board2D.h:217
Aim: A functor Surfel -> Quantity that returns the absolute curvature at given surfel....
Definition VCMGeometricFunctors.h:120