This example shows how to use the fully convex envelope to build a digital polyhedron from an arbitrary mesh. All faces have also the property that their points lies in the naive/standard plane defined by its vertices. It uses DigitalConvexity::relativeEnvelope for computations.
- See also
- Digital polyhedra
For instance, you may call it on object "lion-tri.obj" as
standardDigitalPolyhedronBuilder3D ../examples/samples/lion-tri.obj 0.5 31
The last parameter specifies whether you want to see vertices (1) in black, edges common to both faces (2) in magenta, part of edges that are only on one face (4) and (8) (red on one side, blue on the other) and faces (16) in grey, or any combination.
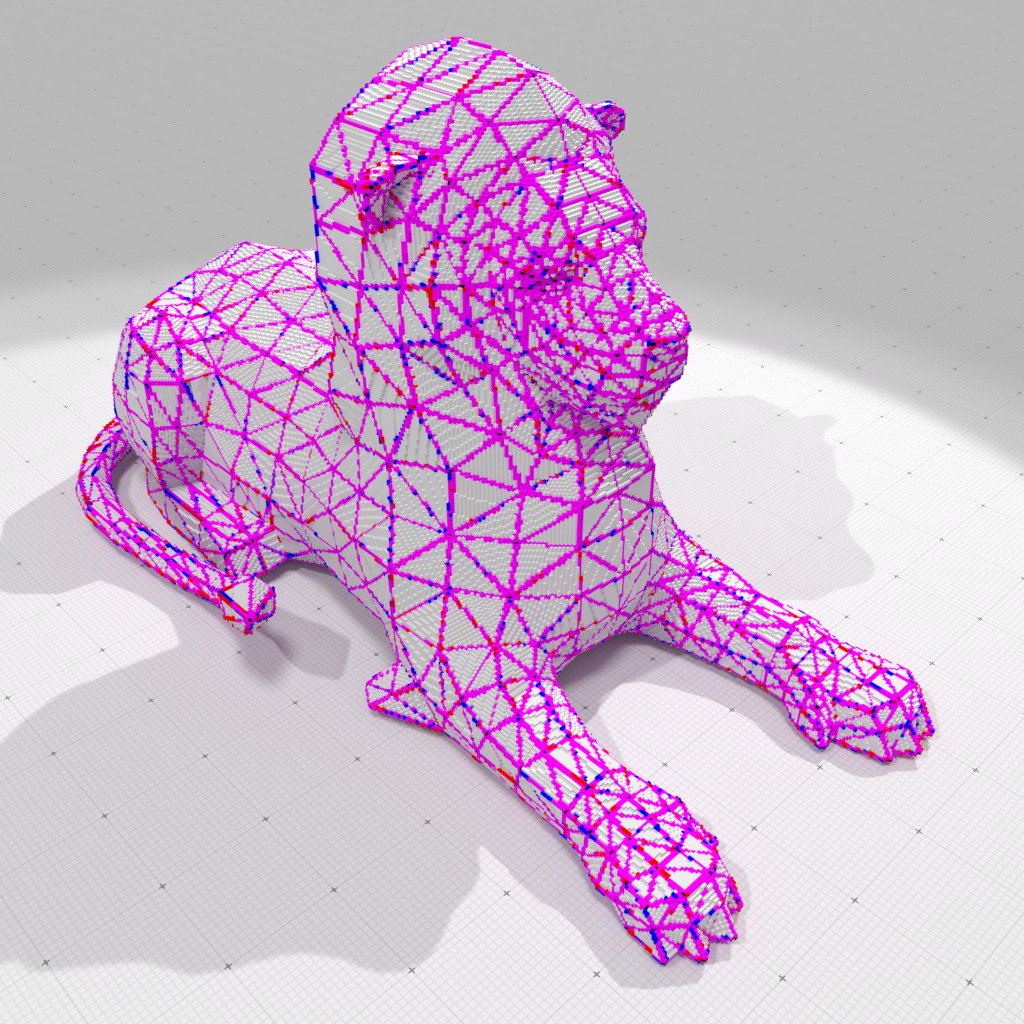
(Symmetric) standard Digital polyhedral model of 'lion-tri.obj' at gridstep 0.5 | 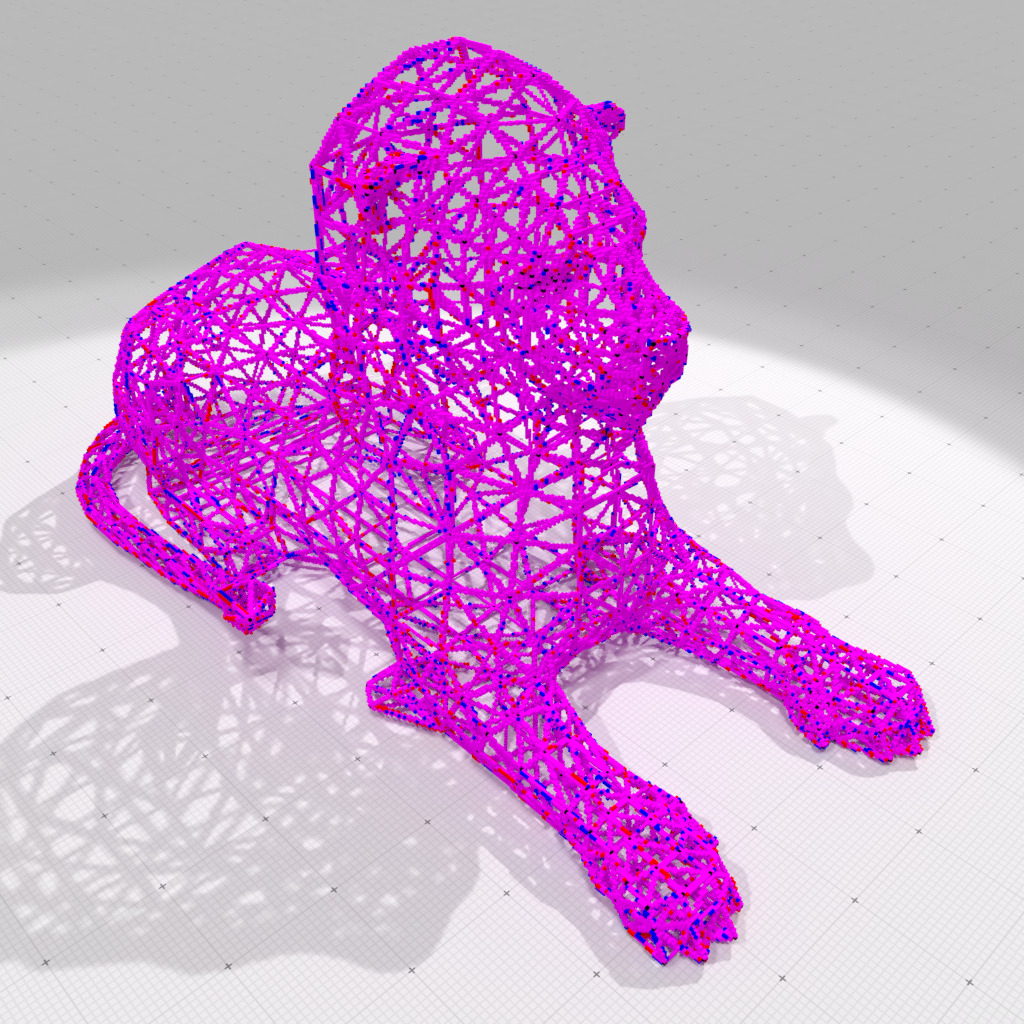
(Symmetric) standard Digital polyhedral model of 'lion-tri.obj' at gridstep 0.5 (vertices and edges only) |
namespace DGtal {
} // namespace DGtal {
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include "DGtal/base/Common.h"
#include "DGtal/helpers/StdDefs.h"
#include "DGtal/io/viewers/Viewer3D.h"
#include "DGtal/shapes/Shapes.h"
#include "DGtal/shapes/SurfaceMesh.h"
#include "DGtal/io/readers/SurfaceMeshReader.h"
#include "DGtal/geometry/volumes/DigitalConvexity.h"
#include "ConfigExamples.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace DGtal;
typedef Space::RealVector RealVector;
// Convenient class to represent different types of arithmetic planes as a predicate.
template < bool Naive, bool Symmetric >
struct MedianPlane {
Vector N;
Integer mu;
Integer omega;
MedianPlane() = default;
MedianPlane( const MedianPlane& other ) = default;
MedianPlane( MedianPlane&& other ) = default;
MedianPlane& operator=( const MedianPlane& other ) = default;
MedianPlane& operator=( MedianPlane&& other ) = default;
: N ( ( q - p ).crossProduct( r - p ) )
{
mu = N.dot( p );
omega = Naive ? N.norm( N.L_infty ) : N.norm( N.L_1 );
if ( Symmetric && ( ( omega & 1 ) == 0 ) ) omega += 1;
mu -= omega / 2;
}
{
auto r = N.dot( p );
return ( mu <= r ) && ( r < mu+omega );
}
};
// Choose your plane !
// typedef MedianPlane< true, false > Plane; //< Naive, thinnest possible
// typedef MedianPlane< true, true > Plane; //< Naive, Symmetric
// typedef MedianPlane< false, false > Plane; //< Standard
{
trace.info() << "\t- view [==31]: display vertices(1), common edges(2), positive side f edges(4), negative side f edges (8), faces(16)" << std::endl;
string filename = examplesPath + "samples/lion.obj";
std::string fn = argc > 1 ? argv[ 1 ] : filename; //< vol filename
double h = argc > 2 ? atof( argv[ 2 ] ) : 1.0;
int view = argc > 3 ? atoi( argv[ 3 ] ) : 31;
// Read OBJ file
std::ifstream input( fn.c_str() );
if ( ! ok )
{
return 1;
}
QApplication application(argc,argv);
MViewer viewer;
viewer.setWindowTitle("standardDigitalPolyhedronBuilder3D");
viewer.show();
Point lo(-500,-500,-500);
Point up(500,500,500);
DigitalConvexity< KSpace > dconv( lo, up );
auto vertices = std::vector<Point>( surfmesh.nbVertices() );
for ( auto v : surfmesh )
{
RealPoint p = (1.0 / h) * surfmesh.position( v );
(Integer) round( p[ 1 ] ),
(Integer) round( p[ 2 ] ) );
vertices[ v ] = q;
}
std::set< Point > faces_set, pos_edges_set, neg_edges_set;
auto faceVertices = surfmesh.allIncidentVertices();
std::vector< Plane > face_planes;
face_planes.resize( surfmesh.nbFaces() );
bool planarity = true;
for ( int f = 0; f < surfmesh.nbFaces() && planarity; ++f )
{
PointRange X;
for ( auto v : faceVertices[ f ] )
X.push_back( vertices[ v ] );
face_planes[ f ] = Plane( X[ 0 ], X[ 1 ], X[ 2 ] );
for ( int v = 3; v < X.size(); v++ )
if ( ! face_planes[ f ]( X[ v ] ) )
{
planarity = false; break;
}
}
if ( ! planarity ) return 1;
for ( int f = 0; f < surfmesh.nbFaces(); ++f )
{
PointRange X;
for ( auto v : faceVertices[ f ] )
X.push_back( vertices[ v ] );
faces_set.insert( F.cbegin(), F.cend() );
for ( int i = 0; i < X.size(); i++ )
{
PointRange Y { X[ i ], X[ (i+1)%X.size() ] };
if ( Y[ 1 ] < Y[ 0 ] ) std::swap( Y[ 0 ], Y[ 1 ] );
int idx1 = faceVertices[ f ][ i ];
int idx2 = faceVertices[ f ][ (i+1)%X.size() ];
// Variant (1): edges of both sides have many points in common
// auto A = dconv.relativeEnvelope( Y, face_planes[ f ], Algorithm::DIRECT );
// Variant (2): edges of both sides have much less points in common
auto A = dconv.relativeEnvelope( Y, F, Algorithm::DIRECT );
bool pos = idx1 < idx2;
(pos ? pos_edges_set : neg_edges_set).insert( A.cbegin(), A.cend() );
}
}
std::vector< Point > face_points, common_edge_points, arc_points, final_arc_points ;
std::vector< Point > pos_edge_points, neg_edge_points, both_edge_points;
std::vector< Point > vertex_points = vertices;
std::sort( vertex_points.begin(), vertex_points.end() );
std::set_symmetric_difference( pos_edges_set.cbegin(), pos_edges_set.cend(),
neg_edges_set.cbegin(), neg_edges_set.cend(),
std::back_inserter( arc_points ) );
std::set_intersection( pos_edges_set.cbegin(), pos_edges_set.cend(),
neg_edges_set.cbegin(), neg_edges_set.cend(),
std::back_inserter( common_edge_points ) );
std::set_union( pos_edges_set.cbegin(), pos_edges_set.cend(),
neg_edges_set.cbegin(), neg_edges_set.cend(),
std::back_inserter( both_edge_points ) );
std::set_difference( faces_set.cbegin(), faces_set.cend(),
both_edge_points.cbegin(), both_edge_points.cend(),
std::back_inserter( face_points ) );
std::set_difference( pos_edges_set.cbegin(), pos_edges_set.cend(),
common_edge_points.cbegin(), common_edge_points.cend(),
std::back_inserter( pos_edge_points ) );
std::set_difference( neg_edges_set.cbegin(), neg_edges_set.cend(),
common_edge_points.cbegin(), common_edge_points.cend(),
std::back_inserter( neg_edge_points ) );
std::set_difference( common_edge_points.cbegin(), common_edge_points.cend(),
vertex_points.cbegin(), vertex_points.cend(),
std::back_inserter( final_arc_points ) );
auto total = vertex_points.size() + pos_edge_points.size()
+ neg_edge_points.size()
+ final_arc_points.size() + face_points.size();
// display everything
Color colors[] =
{ Color::Black, Color::Blue, Color::Red,
Color::Magenta, Color( 200, 200, 200 ) };
if ( view & 0x1 )
{
viewer.setLineColor( colors[ 0 ] );
viewer.setFillColor( colors[ 0 ] );
for ( auto p : vertices ) viewer << p;
}
if ( view & 0x2 )
{
viewer.setLineColor( colors[ 3 ] );
viewer.setFillColor( colors[ 3 ] );
for ( auto p : final_arc_points ) viewer << p;
}
if ( view & 0x4 )
{
viewer.setLineColor( colors[ 1 ] );
viewer.setFillColor( colors[ 1 ] );
for ( auto p : pos_edge_points ) viewer << p;
}
if ( view & 0x8 )
{
viewer.setLineColor( colors[ 2 ] );
viewer.setFillColor( colors[ 2 ] );
for ( auto p : neg_edge_points ) viewer << p;
}
if ( view & 0x10 )
{
viewer.setLineColor( colors[ 4 ] );
viewer.setFillColor( colors[ 4 ] );
for ( auto p : face_points ) viewer << p;
}
viewer << MViewer::updateDisplay;
return application.exec();
}
// //
PointRange relativeEnvelope(const PointRange &Z, const PointRange &Y, EnvelopeAlgorithm algo=EnvelopeAlgorithm::DIRECT) const
Aim: This class is a model of CCellularGridSpaceND. It represents the cubical grid as a cell complex,...
Definition: KhalimskySpaceND.h:394
Definition: SpaceND.h:96
void beginBlock(const std::string &keyword="")
std::ostream & error()
std::ostream & info()
double endBlock()
Definition: Viewer3D.h:132
virtual void show()
Overload QWidget method in order to add a call to updateList() method (to ensure that the lists are w...
DGtal is the top-level namespace which contains all DGtal functions and types.
Definition: ClosedIntegerHalfPlane.h:49
std::pair< typename graph_traits< DGtal::DigitalSurface< TDigitalSurfaceContainer > >::vertex_iterator, typename graph_traits< DGtal::DigitalSurface< TDigitalSurfaceContainer > >::vertex_iterator > vertices(const DGtal::DigitalSurface< TDigitalSurfaceContainer > &digSurf)
STL namespace.
Represents a signed cell in a cellular grid space by its Khalimsky coordinates and a boolean value.
Definition: KhalimskySpaceND.h:209
Aim: An helper class for reading mesh files (Wavefront OBJ at this point) and creating a SurfaceMesh.
Definition: SurfaceMeshReader.h:64
Aim: Represents an embedded mesh as faces and a list of vertices. Vertices may be shared among faces ...
Definition: SurfaceMesh.h:92
void insert(VContainer1 &c1, LContainer2 &c2, unsigned int idx, double v)
Definition: testIndexedListWithBlocks.cpp:52