Loading...
Searching...
No Matches
geometry/volumes/digitalPolyhedronBuilder3D.cpp
This example shows how to use the fully convex envelope to build a digital polyhedron from an arbitrary mesh. It uses DigitalConvexity::envelope for computations.
- See also
- Digital polyhedra
For instance, you may call it on object "spot.obj" as
digitalPolyhedronBuilder3D ../examples/samples/spot.obj 0.005 7
The last parameter specifies whether you want to see vertices (1), edges (2) and faces (4), or any combination.
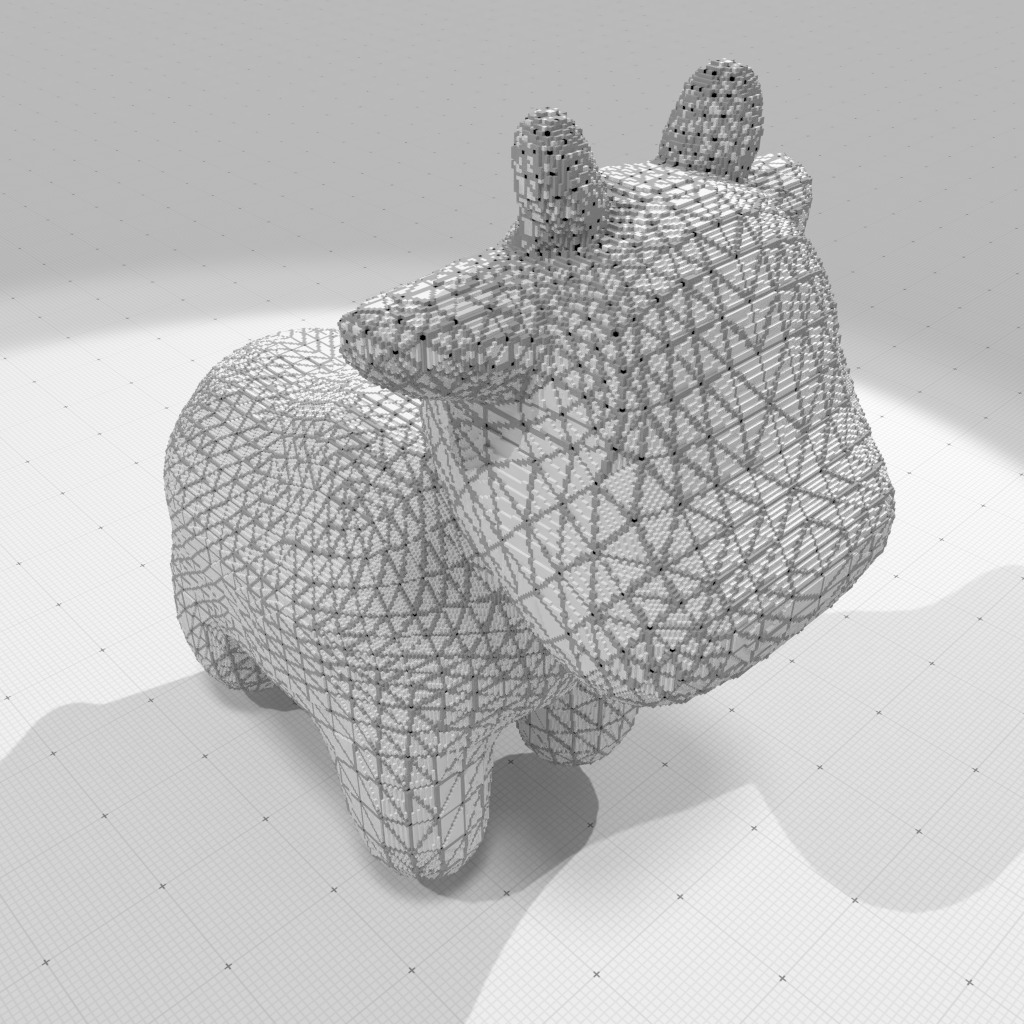
Digital polyhedral model of 'spot.obj' at gridstep 0.005 | 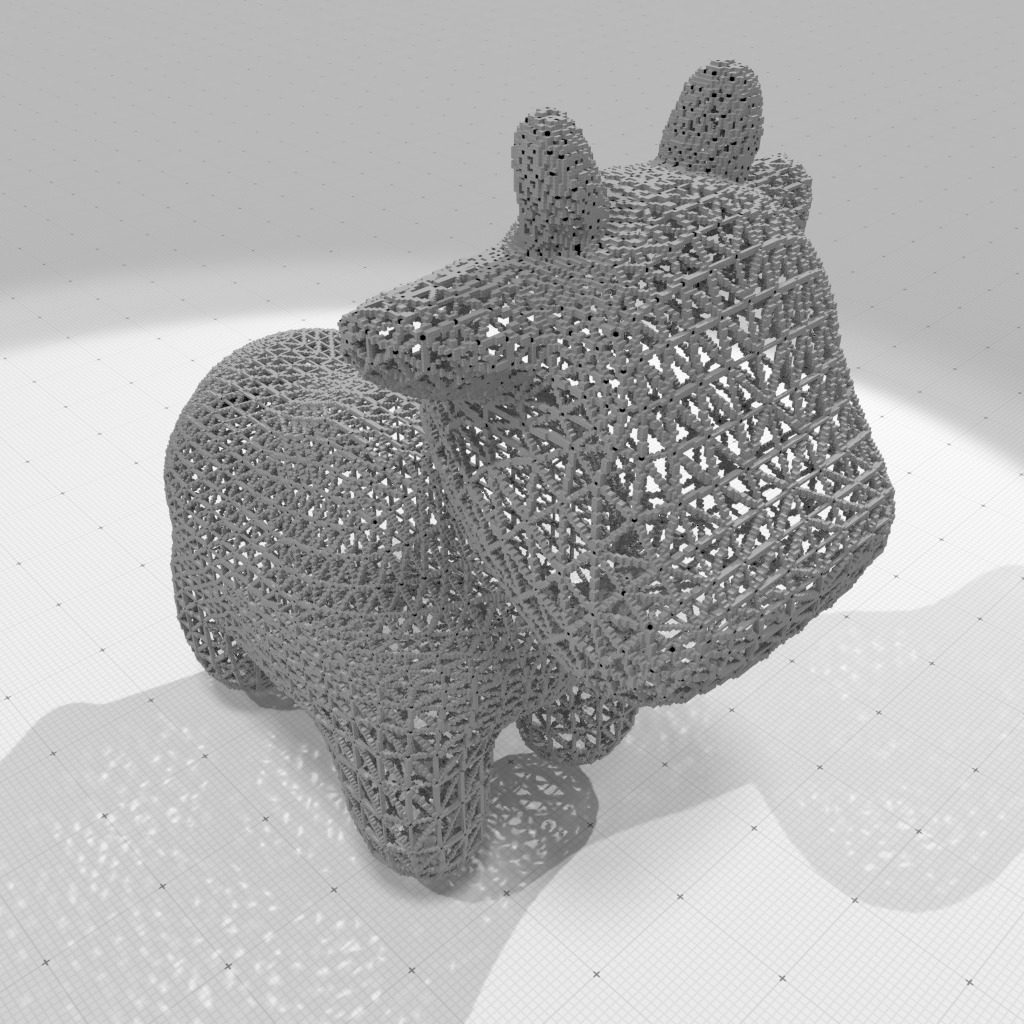
Digital polyhedral model of 'spot.obj' at gridstep 0.005 (vertices and edges only) |
namespace DGtal {
} // namespace DGtal {
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include "DGtal/base/Common.h"
#include "DGtal/helpers/StdDefs.h"
#include "DGtal/io/viewers/PolyscopeViewer.h"
#include "DGtal/shapes/Shapes.h"
#include "DGtal/shapes/SurfaceMesh.h"
#include "DGtal/io/readers/SurfaceMeshReader.h"
#include "DGtal/geometry/volumes/DigitalConvexity.h"
#include "ConfigExamples.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace DGtal;
{
trace.info() << "\tComputes a digital polyhedron from an OBJ file" << std::endl;
trace.info() << "\t- input.obj: choose your favorite mesh" << std::endl;
trace.info() << "\t- h [==1]: the digitization gridstep" << std::endl;
trace.info() << "\t- view [==7]: display vertices(1), edges(2), faces(4)" << std::endl;
string filename = examplesPath + "samples/lion.obj";
std::string fn = argc > 1 ? argv[ 1 ] : filename; //< vol filename
double h = argc > 2 ? atof( argv[ 2 ] ) : 1.0;
int view = argc > 3 ? atoi( argv[ 3 ] ) : 7;
// Read OBJ file
std::ifstream input( fn.c_str() );
if ( ! ok )
{
trace.error() << "Unable to read obj file : " << fn << std::endl;
return 1;
}
typedef PolyscopeViewer<Space,KSpace> MViewer;
MViewer viewer;
Point lo(-500,-500,-500);
Point up(500,500,500);
DigitalConvexity< KSpace > dconv( lo, up );
{
(Integer) round( p[ 1 ] ),
(Integer) round( p[ 2 ] ) );
vertices[ v ] = q;
}
std::set< Point > faces_set, edges_set;
auto faceVertices = surfmesh.allIncidentVertices();
auto edgeVertices = surfmesh.allEdgeVertices();
trace.beginBlock( "Computing polyhedron" );
{
PointRange X;
for ( auto v : faceVertices[ f ] )
X.push_back( vertices[ v ] );
auto F = dconv.envelope( X, Algorithm::DIRECT );
faces_set.insert( F.cbegin(), F.cend() );
}
{
PointRange X =
{ vertices[ edgeVertices[ e ].first ],
vertices[ edgeVertices[ e ].second ] };
auto E = dconv.envelope( X, Algorithm::DIRECT );
edges_set.insert( E.cbegin(), E.cend() );
}
trace.endBlock();
std::vector< Point > face_points, edge_points;
std::vector< Point > vertex_points = vertices;
std::sort( vertex_points.begin(), vertex_points.end() );
std::set_difference( faces_set.cbegin(), faces_set.cend(),
edges_set.cbegin(), edges_set.cend(),
std::back_inserter( face_points ) );
std::set_difference( edges_set.cbegin(), edges_set.cend(),
vertex_points.cbegin(), vertex_points.cend(),
std::back_inserter( edge_points ) );
auto total = vertex_points.size() + edge_points.size() + face_points.size();
trace.info() << "#vertex points=" << vertex_points.size() << std::endl;
trace.info() << "#edge points=" << edge_points.size() << std::endl;
trace.info() << "#face points=" << face_points.size() << std::endl;
trace.info() << "#total points=" << total << std::endl;
// display everything
if ( view & 0x1 )
{
viewer.drawColor( colors[ 0 ] );
viewer.drawColor( colors[ 0 ] );
for ( auto p : vertices ) viewer << p;
}
if ( view & 0x2 )
{
viewer.drawColor( colors[ 1 ] );
viewer.drawColor( colors[ 1 ] );
for ( auto p : edge_points ) viewer << p;
}
if ( view & 0x4 )
{
viewer.drawColor( colors[ 2 ] );
viewer.drawColor( colors[ 2 ] );
for ( auto p : face_points ) viewer << p;
}
viewer.show();
return 0;
}
// //
PointVector< dim, double > RealVector
Definition SpaceND.h:121
DGtal is the top-level namespace which contains all DGtal functions and types.
Definition ClosedIntegerHalfPlane.h:49
Trace trace
std::pair< typename graph_traits< DGtal::DigitalSurface< TDigitalSurfaceContainer > >::vertex_iterator, typename graph_traits< DGtal::DigitalSurface< TDigitalSurfaceContainer > >::vertex_iterator > vertices(const DGtal::DigitalSurface< TDigitalSurfaceContainer > &digSurf)
STL namespace.
Aim: An helper class for reading mesh files (Wavefront OBJ at this point) and creating a SurfaceMesh.
Definition SurfaceMeshReader.h:64